Written by Sara Guevara (Year 9)
Computers. They are such a key part of our lives as humans: they save people’s lives, provide comfort and aid convenience in our daily lives. They are crucial to medicine, scientific research, discoveries and innovations. Computers have played such a vital role in our recent history that it makes you wonder: how different would everything be if it wasn’t for computers? Have they really changed our lives for the better? Would humankind still exist? That last question was a little out there, but they are so integral to our thoughts and routines that it might not be too long until it’s not that far-fetched…
The Invention of the Computer
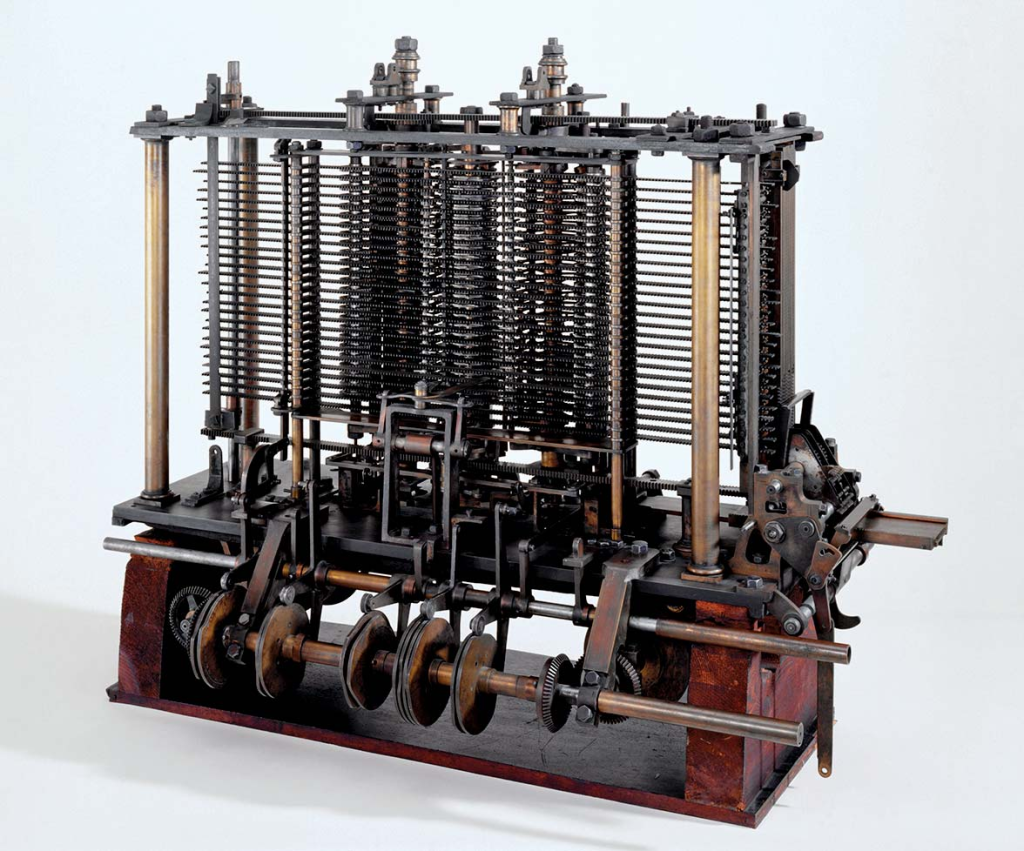
In the year of 1822, the first analog computer was being developed by the English polymath, Charles Babbage. The Difference Engine was able to add, subtract, divide, multiply and then print out hard copies of the results with punch cards (the same method that was used with Jacquard looms at the time). The Difference Engine was, however, never fully built because of a lack of funding. A decade later, in 1833, Babbage realised that a much more complex and powerful computer could be made: the Analytical Engine. It was a more general, fully programmable mechanical computer. The first algorithm that was published would be carried out by the Analytical Engine, with the publisher, Ava Lovelace, the first computer programmer. Though he worked on it until his death in 1871, the Analytical Engine was not fully constructed. Indeed, it was only recently that the computer was finished so that it could be permanently on display in the Science Museum in London.
Analog vs Digital

John Vincent Atanasoff is best known for inventing the first electronic digital computer. Atanasoff invented the first digital computer in the 1930s, at Iowa State University. There was, however, a legal dispute which challenged Atanasoff’s claim that he was the inventor of the first digital computer; it was all resolved in 1971, with the lawsuit ruling that he truly was the creator of the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (also known as ABC).
Analog and digital computers are very different and they are each used for their own purpose. While analog computers use symbols to represent data, digital computers use binary to process data more efficiently. Whereas analog computers are generally slower and have a continuous flow of electrical signals, digital computers are fast, re-programmable and can be switched on and off when needed. Digital computers can also store a lot more information more accurately.
Significant Moments
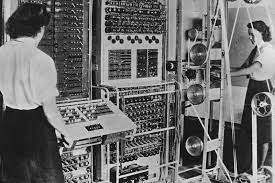
Looking back on some of our recent history, we can see how a monumental breakthrough seems so often to come down to two things: a genius and a computer. Towards the end of World War 2, for example, the British Colossus computer was used to break the German Enigma code. The code gave access to German strategies and helped win the war. Would have the war ended differently if it wasn’t for this machine? Would the world be a different place if it wasn’t for Alan Turing’s code-breaking computer?
“Looking back on some of our recent history, we can see how a monumental breakthrough seems so often to come down to two things: a genius and a computer”
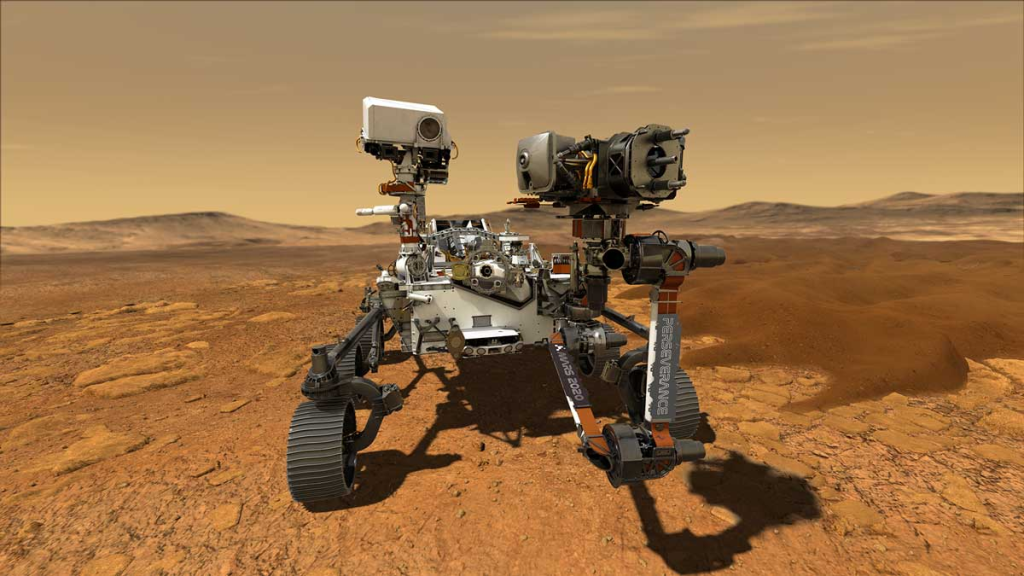
A more recent example of a historical event could be the Curiosity and Perseverance Mars rovers landing in August 2012 and July 2020. The Curiosity rover found that ancient Mars had the right chemistry to support living microbes. Perseverance investigated Jezero Crater, which was a crater lake billions of years ago, providing more evidence that there could have been life on Mars. If it wasn’t for any of the Mars space launches, what would we know about Mars right now? Would we have any sort of information by other means of research?

Modern Day Computer Use
As modern societies are technologically oriented, we use computers for a variety of things in our daily lives too. This has been clearly visible through the Covid-19 outbreak at the end of 2019. With millions of people being sent home, be it from work or from school, everyone has been affected. Not being able to see your family, friends and even co-workers negatively affected the whole world. Yet arguably some good has come out of it. Computers have meant that people can find online meetings more efficient than going into the office. Computers have enabled people to discover new hobbies and share them through social media. Computers have helped us to take time out of the (usually) busy schedules and re-connecting with family, albeit through screens and the internet.
It is not just the internet where computers have changed our daily routines. With electric cars becoming more mainstream and more sustainable, computers and advanced technology are also reducing the damage that we are doing to our planet. The famous MINI Oxford plant, for example, released its fully electric model just last year! While it is still not perfect, the sustainable nature of technology continues to advance and develop as time goes on.
The Future of Computers
AI is the future. Be it self-driving cars or robots replacing factory jobs, research and innovation continues to advance at pace. These advances are not far off. Robots are already being programmed to read human emotion and expression to help in education; virtual tutors will help real life teachers to understand their students’ emotions to help determine who is struggling or who is bored, then allow the teacher to help each student with their individual needs. Google is working on an AI assistant that will place human-like calls for an appointment somewhere, making everything simply more convenient.

Final Thoughts
As you’ve probably figured, computers are a pretty big part of our modern history, our present and surely our future too. Acknowledging that this increasing reliance on computers is happening is one thing but forming your own opinion is another. Is it doing more harm than good? Or is this key to humankind’s evolution? You decide.